
What is Orthognathic treatment?
Orthognathic treatment is an operation to reposition either the upper, lower, or both jaws, in individuals who have a large discrepancy between the size of the jaws in relation to each other, or in whom the jaws are abnormally positioned in relation to the base of skull.
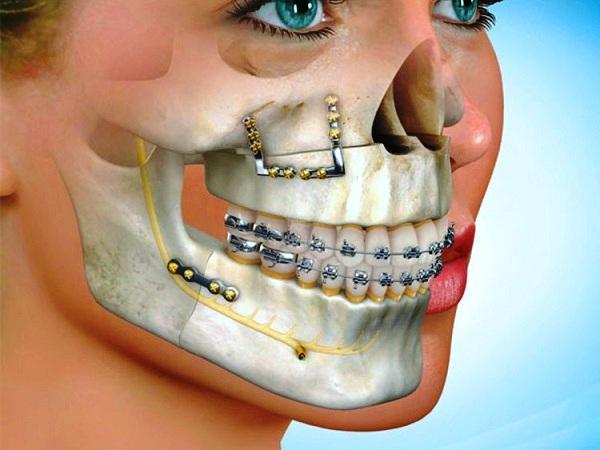
How are people who have these abnormal jaw relationships affected?
Individuals affected will usually have a malocclusion (poorly aligned teeth and bite) which mostly can be treated using orthodontics (braces) alone. However a small proportion of individuals with severe jaw discrepancies often have significant facial deformity and can be affected in many ways:
- High levels of psychological distress, affecting interpersonal relationships and quality of life.
- Difficulty eating certain foods
- Jaw muscle and jaw joint problem
- Speech difficulties
What causes a jaw discrepancy?
- Without a specific cause
- May be a family history
- Result of a growth disturbance such as a jaw fracture in childhood or repair of a cleft lip or palate.
- Can be associated with a syndrome such as hemifacial microsomia.
A jaw discrepancy may be detected in early childhood but usually becomes more marked during puberty. The unusual jaw growth usually ceases in late adolescence and treatment is directed towards correction of the deformity once growth is complete.
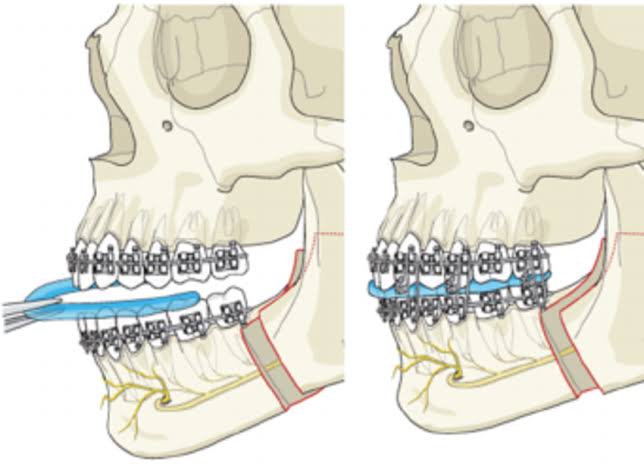
Type of Orthognathic surgery approach
1.Surgery-First Approach
“Immediate improvement of facial esthetics, less treatment time”
Advantage of Surgery-First approach
- Achieve immediate improvement in facial appearance
- Reducing the overall treatment time
2.Traditional approach
3 stages involve
- Pre-surgical orthodontic treatment to relieve the dental compensations
- Orthognathic surgical procedure
- Post-surgical orthodontics to finish the case and settle the occlusion
The disadvantages of having orthodontic interventions both before and after orthognathic surgery
- Long treatment time
- Temporary worsening of facial appearance Patients become discouraged.








